SayviethaBT
Member
Universal Banking: A One-Stop Financial Supermarket
In the evolving world of finance, the concept of Universal Banking has emerged as a transformative model that brings together a wide range of financial services under one roof. Unlike traditional banking systems that limit their services to deposits and loans, universal banks offer a much broader spectrum, including investment services, insurance, asset management, and more.
This article explores what universal banking is, its features, advantages, potential drawbacks, global examples, and its significance in modern economies.
What is Universal Banking?
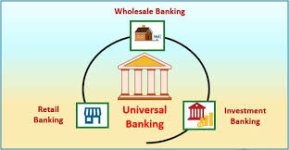
Universal Banking refers to a financial system where banks offer a wide variety of services such as commercial banking, investment banking, insurance, and other financial products through a single entity. It allows customers—both individuals and corporations—to access a wide range of financial services from a single institution.
This model contrasts with the traditional approach where different institutions handled different aspects of finance—commercial banks focused on deposits and loans, while investment banks managed stocks, bonds, and other securities.
Key Features of Universal Banking
- Diversified Services: Universal banks offer services like savings and current accounts, personal and business loans, mutual funds, stock brokerage, insurance policies, investment advice, wealth management, and retirement planning.
- Single Institution Convenience: Customers benefit from a single platform for multiple services, simplifying financial management.
- Cross-Selling Opportunities: Universal banks can cross-sell various financial products to their existing customer base, improving customer retention and profitability.
- Economies of Scale: By operating across various financial sectors, universal banks can reduce costs and improve efficiency through shared infrastructure and personnel.
- Global Reach: Many universal banks operate globally, offering clients access to international markets and financial products.
Services Provided by a Universal Bank
- Retail Banking: Savings accounts, personal loans, credit cards, etc.
- Corporate Banking: Business loans, treasury management, trade finance.
- Investment Banking: Underwriting, mergers and acquisitions, stock and bond issuance.
- Insurance Services: Life insurance, health insurance, general insurance.
- Asset Management: Mutual funds, portfolio management, wealth advisory.
- Forex and Treasury: Foreign exchange services, interest rate hedging, commodity trading.
Advantages of Universal Banking
- Customer Convenience
Having a single bank manage all your financial needs is highly convenient. From checking accounts to investment advice, everything is under one roof. - Lower Transaction Costs
Universal banks benefit from economies of scale, which helps in lowering the cost of services for customers. - Better Risk Management
Since universal banks operate in diverse areas, they can balance the risks—losses in one sector might be compensated by profits in another. - Improved Financial Inclusion
These banks often operate large networks, helping bring financial services to underserved and rural areas. - Increased Profits for Banks
The ability to sell multiple products to the same customer base leads to higher profitability.
Disadvantages of Universal Banking
- Too Big to Fail
Large universal banks may pose systemic risks. If one fails, it could lead to widespread financial instability, as seen during the 2008 global financial crisis. - Conflicts of Interest
Combining investment and commercial banking can lead to conflicts—for instance, when banks promote financial products for their benefit rather than the client’s. - Complexity and Mismanagement
Managing such a vast range of services can lead to operational complexities and mismanagement. - Lack of Personalized Service
Big universal banks may lack the personal touch and customer service focus found in smaller, specialized banks.
Examples of Universal Banks
Several major financial institutions globally operate on the universal banking model:
- Citigroup (USA)
- JPMorgan Chase (USA)
- Barclays (UK)
- HSBC (UK)
- Deutsche Bank (Germany)
- UBS (Switzerland)
- ICICI Bank and State Bank of India (SBI) (India)
These banks provide a wide array of financial services to individuals, businesses, and governments across the world.
Universal Banking in India
The concept of universal banking was formally introduced in India in the early 2000s, following the recommendations of the Narasimham Committee and the RBI (Reserve Bank of India).
Prominent Indian banks such as ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, and HDFC Bank have embraced the universal banking model. These banks now offer services ranging from basic savings accounts to mutual funds, insurance, and wealth management—all under one brand.
The shift towards universal banking in India was aimed at making the banking sector more competitive, robust, and customer-friendly.
The Future of Universal Banking
With the rise of FinTech (financial technology), digital transformation, and customer expectations for integrated services, the universal banking model continues to evolve. Many traditional banks are partnering with FinTech firms to provide innovative solutions, such as mobile banking apps, robo-advisors, and AI-powered customer service.
In the future, universal banks may become more tech-driven, data-focused, and customer-centric. However, they will need to navigate regulatory changes, cybersecurity threats, and growing competition from digital-only banks.
Conclusion
Universal banking is like a financial supermarket that provides a variety of services under one roof. It offers convenience, cost-efficiency, and integrated financial solutions to customers. While it brings many benefits to both banks and consumers, it also comes with challenges such as potential conflicts of interest and systemic risks.
Despite these challenges, universal banking has become a dominant model in the global financial industry and is likely to shape the future of banking by offering holistic financial services in an increasingly interconnected world.