THE[/b]
CHANGE CAPABILITY INDEX (HCCI)[/b]
AN[/b]
ORGANIZATIONAL MATURITY DIAGNOSTIC[/b]
&[/b]
Development Program[/b]
[/b]
TO[/b]
IMPROVE TRACTION & SUSTAINABILITY[/b]
FOR CHANGE & GROWTH INTERVENTIONS[/b]
[/b]
[/b]
[/b]
An Introduction[/b]
by[/b]
Dr. Myles Sweeney[/b]
Mr. Declan Kavanagh[/b]
Introduction to Holignment’s Change Capability Index (HCCI)
Change is unavoidable for organizations. But, it is something that many organizations do poorly. Research shows 70% failure rates for change and growth initiatives (McKinsey). The reason is simple. Failure occurs when initiatives overstep the Capability (Capacity & Competence) for change in the organization. Now, this can change. Holignment measures the change Capability in the organization, or relevant section. For the first time, a science-based approach graphically shows the weak-spots in organizational functioning and gives a 10-step roadmap that will improve change-program outcomes and the overall Capability of the organisation to manage and adapt to change.
Improve your organisation’s Capability to change, achieve Leadership levels, where your organisation is change-comfortable, proactive and responsive. Diagnose your organisation’s change Capability and if you reside in the top half you can execute change and take the recommended steps in parallel to achieve a Leadership position. However if the functioning of your organisation (or a section of it) resides in the lower half of the model, your change Capability will be limited or non-existent, and extra attention will be required to organisation development prior to making the specific business change.
This is an important new insight into the challenge facing CEOs and their organisations who stand to gain so much with effective change. The Model explains for the first time why failure rates are so high for change, and how to remedy it.
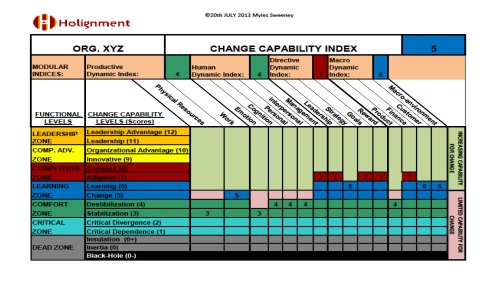
Fig. 1. Sample Dashboard
Each Growth Dynamic (seen above as diagonal titles) comprises 5 or more Dynamic Constructs. For example, Cognition has Decision Making, Planning, Communicating, etc. Another key insight of the approach is that Sustainable Change and Growth can only occur at the level of the Construct, with organizational change and development arising as an integrated accrual of such changes.
The solution is simple. Run an on-line diagnostic survey, use the automatically generated instructions to plug the gaps and know that you have a strong organizational system. Furthermore, the instructions for each dimension give step-by-step guidance to achieve the highest levels of its developmental programme for as much of the organization to which it is applied – Sustainable Competitiveness, Organizational Advantage and ultimately, Leadership Advantage.
For any kind of change-management intervention small or large throughout an organization, the HCMMI tool based on Levels of Learning[/i] theory and designed specifically to optimise traction and sustainability which have been found to be missing from typical initiatives that contribute to the high failure rates for Change-Management interventions.
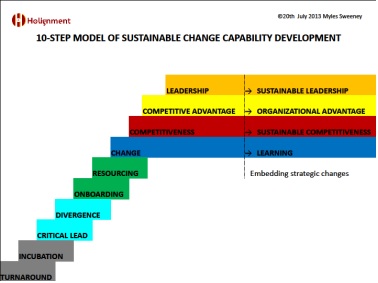
Fig. 2. Holignment Model for developing Change Capability
How does it work?
1. The leadership and management have identified the need to understand the change Capability across the organisation with a view to pro actively improving the outcome for a specific change initiative and whatever change might be needed thereafter
2. Targeted participants (i.e., some or all of the organisation) complete online diagnostic questionnaires. The resultant data automatically generates a visual dashboard and report of the change Capability for the organisation overall and/or whatever sections have been targeted.
3. Using the step-by-step instructions of the reports, management now implement interventions appropriate to the change Capability within the target organisation or sub set/group thereby, improving change Capability and the sustainability of the growth arising from the change initiative once implemented
4. (Diagnosed in the Change-Capable (top) half of the Model)[/i][/b] The natural order of change-Capability development is to select and implement the recommended interventions for the next level up from the measured functioning level.
5. (Diagnosed in the Change-Limited (Lower) half of the Model)[/i][/b] If the level of functioning is diagnosed as habituated, it is normally necessary to build the interventions from Level 1 of the programme which is called the Turnaround Level. This is because for the change to be successful, the factors that have cause functioning to stall will have to be collectively rejected and the functioning in question re-developed through all of the Levels.
6. Following the change and periodically thereafter, management can survey and understand the effectiveness of the change and ongoing change Capability thus establishing its overall change Capability as well as its potential for sustainable growth.
Using this method allows management to calibrate the specific change interventions to the level the organisation or section is functioning at, while improving change Capability. The use of the model also signals to stakeholders the importance of change and their involvement in the process.
Some Examples of change where the Model & Process should be considered[/i][/b]
Strategic Change
§ In or Out-Sourcing
§ Corporate Program
§ Turnaround Strategy
§ Growth Strategy
§ M & A activity
§ Divestment
§ Rightsizing
Routine Operational Change
§ New Product or Service Introduction
§ Continuous Improvement or Lean Program initiated change
§ Significant New Customer or Supplier
§ Starting a New Team or Function
§ Changing a Business Process
§ Introducing a New Team Member or Leader
§ Collaboration Program or Platform
§ Introducing a New IT system
Change is a naturally occurring daily and periodic process in most organisations. However, there is a tendency to develop an accepted status-quo, and this can occur at any level in the model. Therefore, to effect any of the change examples below we may have to move stakeholders out of a habituated level in the only way that gives any Change program traction i.e., within a growth process which ensures better outcomes from the initiative.
Mo[/b][/i]del Overview & Terminology[/i][/b]
Description of Change Capability Levels[/b]
1. BLACK HOLE
a. Diagnostic Findings
This is the lowest level of functioning. For dimensions reported at this level, resources are being haemorrhaged, morale is at distress levels, while attitude can be anti-growth and even destructive toward organizational interests
b. Symptoms
Embezzling Managers, Undisciplined Staff, Loss-Making Projects, Destructive Environmental Footprint, Antagonism towards customers, etc.
c. Remedy
Level 1 TURNAROUND - A Collective Decision to disconnect from the old.
Typical actions and process steps might include:
i)
