SayviethaBT
Member
GMAT Exam: Gateway to Global Business Education
In today's competitive world, aspiring business professionals seek avenues that can lead them to world-class management education. One such powerful stepping stone is the GMAT – the Graduate Management Admission Test. The GMAT is recognized globally and plays a vital role in gaining admission to prestigious business schools for MBA and other management programs.This article provides a comprehensive understanding of the GMAT exam, including its purpose, format, eligibility, benefits, and effective preparation strategies.
What is the GMAT Exam?
The GMAT is a standardized computer-based exam administered by the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC). It is widely accepted by over 2,300 business schools and more than 7,000 programs worldwide, including MBA, Master of Finance, and Master of Accountancy programs.The exam assesses a candidate's analytical writing, quantitative reasoning, verbal reasoning, and integrated reasoning skills — all of which are considered essential for success in graduate business education.
Why is the GMAT Important?
Here’s why the GMAT holds great significance for students and professionals planning to pursue business education:- Admission to Top B-Schools: Most globally ranked B-schools, including Harvard, Stanford, INSEAD, Wharton, and London Business School, require GMAT scores for admissions.
- Scholarship Opportunities: A high GMAT score can enhance the chances of securing scholarships or financial aid.
- Career Growth: A strong GMAT score adds weight to a candidate’s profile, making them more attractive to global employers.
- Standardized Benchmark: The GMAT offers a level playing field for candidates across different educational and cultural backgrounds.
- Flexibility: The GMAT can be taken at test centers or online, with the flexibility to choose the order of sections.
Eligibility Criteria
There are no specific academic qualifications required to take the GMAT. However, here are some general eligibility guidelines:- The candidate must be at least 18 years old. If between 13 to 17, parental consent is required.
- Candidates should possess a bachelor’s degree or be in the final year of their undergraduate program.
- There is no upper age limit or work experience required, but most MBA programs prefer candidates with 2-5 years of work experience.
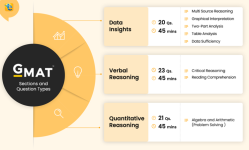
GMAT Exam Structure
The GMAT consists of four sections, and the exam lasts approximately 3 hours and 7 minutes, excluding breaks:| Section | Time | Questions | Score Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Writing Assessment | 30 minutes | 1 essay | 0–6 |
| Integrated Reasoning | 30 minutes | 12 questions | 1–8 |
| Quantitative Reasoning | 62 minutes | 31 questions | 6–51 |
| Verbal Reasoning | 65 minutes | 36 questions | 6–51 |
- Total GMAT Score: The combined score ranges from 200 to 800, based on Quantitative and Verbal scores.
Understanding the Sections
- Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA)
- Tests your ability to analyze an argument and communicate your thoughts effectively.
- Involves writing a single essay
- Integrated Reasoning (IR)
- Measures your ability to evaluate information presented in multiple formats (charts, tables, graphs, etc.).
- Includes multi-source reasoning and data interpretation questions.
- Quantitative Reasoning
- Tests basic math skills and logical reasoning.
- Topics include arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and word problems.
- Verbal Reasoning
- Tests grammar, comprehension, and critical reasoning.
- Includes sentence correction, reading comprehension, and logical argument analysi
GMAT Registration Process
- Visit the official GMAT website: www.mba.com.
- Create a GMAT account and choose your preferred exam date and location (test center or online).
- Pay the registration fee of $275 USD (may vary by country).
- You can take the GMAT up to 5 times in 12 months, but no more than 8 times in total.
How to Prepare for GMAT
Know the Format: Understand the question types and structure of each section.
Create a Study Plan: Allocate 2-3 months of focused preparation.
Use Official Resources: Utilize GMAC’s official guides, practice tests, and question banks.
Practice Regularly: Solve mock tests to improve speed, accuracy, and time management.
Analyze Mistakes: Review your errors to avoid repeating them.
Join Study Groups/Coaching: For guidance and peer learning, join a GMAT preparation course or online community.
Tips for Success
- Time Management is critical — allocate time wisely during each section.
- Don’t skip AWA or IR — some schools consider these sections too.
- Use the Score Preview Option to decide whether to report or cancel your score after the exam.
- Leverage GMAT Online, especially if you prefer the flexibility of taking the test from home.
Conclusion
The GMAT is more than just an entrance test; it's a stepping stone to an exciting and successful career in the world of business and management. With a well-planned strategy and consistent effort, cracking the GMAT is achievable. Whether you're planning to study in the U.S., Europe, or Asia, a good GMAT score can unlock opportunities at the best business schools around the world.So, if an MBA or a management career is on your radar, it’s time to start your GMAT journey today!