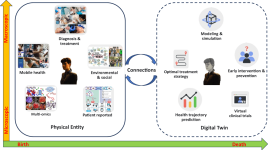
The emergence of digital twin technology is reshaping the healthcare industry by providing real-time, data-driven 3D visualizations that mirror the state of physical patients, devices, or systems. Computer graphics play a critical role in bringing these digital twins to life, enabling professionals to simulate, monitor, and predict complex medical scenarios within a virtual framework.
A digital twin in healthcare refers to a digital replica of a physical object, system, or patient. It is continuously updated with real-world data from sensors, medical devices, and patient health records. By using advanced computer graphics, these digital models are rendered with incredible detail, making them interactive, dynamic, and visually interpretable by clinicians and engineers alike.
One of the most revolutionary uses of digital twin visualizations is in patient-specific care. For instance, a heart surgeon can view a 3D model of a patient’s cardiovascular system created from MRI or CT scan data. This allows for simulated surgeries, risk assessments, and treatment planning with improved accuracy and reduced human error. These models can visualize blood flow, identify blockages, or even simulate the placement of a stent before the real procedure occurs.
Hospitals are also leveraging digital twins to manage infrastructure and workflows. A digital twin of a hospital floor, powered by real-time data from IoT devices, can visualize patient flow, equipment status, and room availability. The 3D interface helps healthcare managers optimize resource allocation, reduce bottlenecks, and ensure faster emergency response. By embedding AI-driven analytics into these systems, future trends or emergencies can also be predicted graphically.
Another valuable application lies in chronic disease management. Patients with conditions like diabetes or asthma can be monitored remotely, with their digital twin reflecting real-time updates such as glucose levels, medication intake, and symptom reports. These visualizations enable doctors to track the progress and predict potential health risks—visually highlighting issues before they escalate.
Digital twin graphics are also transforming medical training. Students can interact with 3D anatomical models that behave like real human systems. For instance, a virtual lung that inflates and deflates with each breath, responding to simulated stimuli like pollutants or medicine. These immersive simulations promote better understanding and retention compared to traditional static diagrams or textbooks.
Despite the benefits, the use of digital twins in healthcare also raises concerns. Data privacy is a major issue, as real-time monitoring relies on continuous patient data transmission. Additionally, building accurate, high-resolution digital twins requires robust computing power, skilled personnel, and interdisciplinary collaboration between medical professionals, graphic designers, and software developers.
The potential of digital twin visualizations in healthcare is enormous. As the technology matures, we are likely to see more patient-centered applications where individuals have access to their own digital twins. These could offer suggestions for lifestyle improvements, alert users about health risks, or even interact with wearable devices to provide live feedback.
Join the Conversation:
Have you heard of digital twins in medicine before?
Would you feel comfortable having a real-time 3D model of your body monitored by doctors?
How do you see this technology shaping the future of healthcare?
Let us know your thoughts in the comments!
A digital twin in healthcare refers to a digital replica of a physical object, system, or patient. It is continuously updated with real-world data from sensors, medical devices, and patient health records. By using advanced computer graphics, these digital models are rendered with incredible detail, making them interactive, dynamic, and visually interpretable by clinicians and engineers alike.
One of the most revolutionary uses of digital twin visualizations is in patient-specific care. For instance, a heart surgeon can view a 3D model of a patient’s cardiovascular system created from MRI or CT scan data. This allows for simulated surgeries, risk assessments, and treatment planning with improved accuracy and reduced human error. These models can visualize blood flow, identify blockages, or even simulate the placement of a stent before the real procedure occurs.
Hospitals are also leveraging digital twins to manage infrastructure and workflows. A digital twin of a hospital floor, powered by real-time data from IoT devices, can visualize patient flow, equipment status, and room availability. The 3D interface helps healthcare managers optimize resource allocation, reduce bottlenecks, and ensure faster emergency response. By embedding AI-driven analytics into these systems, future trends or emergencies can also be predicted graphically.
Another valuable application lies in chronic disease management. Patients with conditions like diabetes or asthma can be monitored remotely, with their digital twin reflecting real-time updates such as glucose levels, medication intake, and symptom reports. These visualizations enable doctors to track the progress and predict potential health risks—visually highlighting issues before they escalate.
Digital twin graphics are also transforming medical training. Students can interact with 3D anatomical models that behave like real human systems. For instance, a virtual lung that inflates and deflates with each breath, responding to simulated stimuli like pollutants or medicine. These immersive simulations promote better understanding and retention compared to traditional static diagrams or textbooks.
Despite the benefits, the use of digital twins in healthcare also raises concerns. Data privacy is a major issue, as real-time monitoring relies on continuous patient data transmission. Additionally, building accurate, high-resolution digital twins requires robust computing power, skilled personnel, and interdisciplinary collaboration between medical professionals, graphic designers, and software developers.
The potential of digital twin visualizations in healthcare is enormous. As the technology matures, we are likely to see more patient-centered applications where individuals have access to their own digital twins. These could offer suggestions for lifestyle improvements, alert users about health risks, or even interact with wearable devices to provide live feedback.
Join the Conversation:
Have you heard of digital twins in medicine before?
Would you feel comfortable having a real-time 3D model of your body monitored by doctors?
How do you see this technology shaping the future of healthcare?
Let us know your thoughts in the comments!