Have you ever wondered what the lost city of Pompeii or the ancient Library of Alexandria really looked like? With the advancement of computer graphics, it's no longer just imagination—3D simulations can bring centuries-old structures back to life with remarkable accuracy.
Using digital tools, researchers and historians are now able to reconstruct ancient buildings, monuments, and entire cities, allowing us to explore history like never before. These simulations do more than satisfy curiosity—they preserve cultural heritage and revolutionize historical education.
Historical architecture is often found in ruins or incomplete fragments. Physical restoration is expensive, invasive, and sometimes impossible. 3D graphics offer a non-invasive, reversible, and scalable solution for visualizing the past while preserving the present.
Simulations are used for:
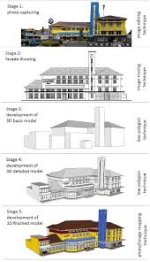
These techniques collect real-world measurements by capturing thousands of photographs or using lasers to map surfaces. The data is then processed using CG tools like Agisoft Metashape or RealityCapture to create accurate 3D models.
Designers use tools like Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, and SketchUp to digitally reconstruct buildings based on blueprints, texts, archaeological data, and visual references.
Adding textures that replicate real-world materials (brick, marble, wood) and simulating lighting based on historical settings (torches, oil lamps, sun direction) adds realism.
By using VR headsets, viewers can walk through historical spaces, explore architecture from different eras, and even interact with simulated environments.
Balancing educational goals with responsible representation is essential in the use of 3D graphics for historical topics.
Have you explored any historical reconstructions in VR or online?
Do you think digital simulations can replace physical visits to historical sites?
What ancient structure would you love to see brought to life through computer graphics?
Share your thoughts in the comments!
Using digital tools, researchers and historians are now able to reconstruct ancient buildings, monuments, and entire cities, allowing us to explore history like never before. These simulations do more than satisfy curiosity—they preserve cultural heritage and revolutionize historical education.
Why Simulate Historical Architecture?
Historical architecture is often found in ruins or incomplete fragments. Physical restoration is expensive, invasive, and sometimes impossible. 3D graphics offer a non-invasive, reversible, and scalable solution for visualizing the past while preserving the present.
Simulations are used for:
- Educational experiences in schools and museums
- Supporting archaeological research
- Virtual tourism and heritage promotion
- Documentary filmmaking and cultural storytelling
- Restoration planning by architects and conservationists
Technologies Behind the Magic
1.
These techniques collect real-world measurements by capturing thousands of photographs or using lasers to map surfaces. The data is then processed using CG tools like Agisoft Metashape or RealityCapture to create accurate 3D models.
2.
Designers use tools like Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, and SketchUp to digitally reconstruct buildings based on blueprints, texts, archaeological data, and visual references.
3.
Adding textures that replicate real-world materials (brick, marble, wood) and simulating lighting based on historical settings (torches, oil lamps, sun direction) adds realism.
4.
By using VR headsets, viewers can walk through historical spaces, explore architecture from different eras, and even interact with simulated environments.
Case Studies of Digital Reconstruction
- Rome Reborn: A project aiming to digitally recreate Ancient Rome as it appeared in 320 AD, including the Colosseum, the Roman Forum, and imperial palaces.
- The Temple of Karnak (Egypt): Researchers used 3D graphics to simulate the temple complex’s original layout and hieroglyphs.
- Machu Picchu Virtual Tour: A 3D online walkthrough of the Incan citadel using drone photography and graphics mapping.
Benefits of Simulating Historical Architecture
- Educational Value: Enables interactive learning through visual storytelling.
- Preservation Without Damage: Avoids physical alteration of fragile sites.
- Accessibility: Allows global access to cultural heritage via digital platforms.
- Tourism Support: Encourages interest and funding for conservation efforts.
- Time Travel for Researchers: Offers a tool for testing hypotheses about how spaces were used or constructed.
Ethical Considerations
- Accuracy vs. Artistic License: How much guesswork is acceptable when recreating lost details?
- Cultural Sensitivity: Are simulations respectful and properly contextualized?
- Ownership of Digital Heritage: Who controls the access and use of these reconstructions?
Balancing educational goals with responsible representation is essential in the use of 3D graphics for historical topics.
The Future of Historical Simulation
- AI-Assisted Restoration: Machine learning will help predict missing architectural features based on patterns from similar structures.
- Holographic Displays: Museums may soon showcase full-scale holographic buildings that appear and vanish with the press of a button.
- Crowdsourced Cultural Modeling: Enthusiasts and historians could collaborate to simulate lesser-known local heritage sites.
Join the Conversation
Have you explored any historical reconstructions in VR or online?
Do you think digital simulations can replace physical visits to historical sites?
What ancient structure would you love to see brought to life through computer graphics?
Share your thoughts in the comments!