Driving simulators are no longer confined to video games—they are now powerful tools used in driver training, vehicle design, autonomous vehicle testing, and even neurological therapy. The realism and effectiveness of these simulators heavily depend on one crucial component: the graphic engine.
Graphic engines, also known as rendering engines, are responsible for creating the virtual environments, vehicle dynamics, lighting conditions, and realistic visual effects that make a simulator feel like the real world. Whether used in training centers or research labs, these engines form the backbone of immersive driving experiences.
A graphic engine is software designed to render 2D or 3D visuals in real time. In driving simulators, it’s used to:
The engine processes user inputs (steering, acceleration, braking) and translates them into dynamic changes within the simulated environment.
Engines support photorealistic textures for roads, signs, weather, and foliage, creating a believable environment.
Realistic car movement, suspension response, and collision dynamics improve learning and training accuracy.
Engines can simulate rain, fog, snow, day-night cycles, and even glare from the sun, which helps train users under diverse driving scenarios.
Advanced AI algorithms simulate pedestrians, other vehicles, and traffic rules, offering dynamic responses to driver decisions.
These advancements aim to make simulators indistinguishable from real driving experiences.
Have you ever used a driving simulator for training or gaming?
Do you think simulation-based driving tests could replace real-world trials in the future?
What features would you love to see in the next generation of driving simulators?
Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Graphic engines, also known as rendering engines, are responsible for creating the virtual environments, vehicle dynamics, lighting conditions, and realistic visual effects that make a simulator feel like the real world. Whether used in training centers or research labs, these engines form the backbone of immersive driving experiences.
What Is a Graphic Engine?
A graphic engine is software designed to render 2D or 3D visuals in real time. In driving simulators, it’s used to:
- Render lifelike roads, buildings, and traffic
- Simulate weather, lighting, and time-of-day changes
- Display accurate vehicle movement and surroundings
- Ensure smooth interactions between user controls and visual output
The engine processes user inputs (steering, acceleration, braking) and translates them into dynamic changes within the simulated environment.
Popular Graphic Engines Used in Driving Simulators
1. Unity3D
- Widely used in both gaming and simulation.
- Supports real-time rendering, VR integration, and physics-based vehicle behavior.
- Extensively customizable for creating different driving scenarios.
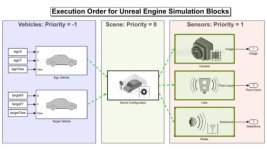
2. Unreal Engine
- Offers cinematic quality visuals with advanced lighting and shaders.
- Suitable for high-end simulators, especially for training and automotive R&D.
- Includes blueprint scripting for rapid prototyping.
3. CARLA (Car Learning to Act)
- An open-source simulator designed specifically for autonomous driving research.
- Used for AI training, traffic rule enforcement, and obstacle avoidance.
- Based on Unreal Engine, it provides realistic city and highway environments.
4. OpenDS (Open Driving Simulator)
- Open-source, Java-based platform for driving research.
- Used in cognitive science, human factors research, and road safety studies.
- Allows integration with physiological sensors for detailed data analysis.
How Graphic Engines Impact Realism
✔ High-Quality Textures
Engines support photorealistic textures for roads, signs, weather, and foliage, creating a believable environment.
✔ Physics Simulation
Realistic car movement, suspension response, and collision dynamics improve learning and training accuracy.
✔ Weather & Time Conditions
Engines can simulate rain, fog, snow, day-night cycles, and even glare from the sun, which helps train users under diverse driving scenarios.
✔ Interactive Traffic
Advanced AI algorithms simulate pedestrians, other vehicles, and traffic rules, offering dynamic responses to driver decisions.
Applications of Driving Simulators
- Driver Training: Especially for beginners, army drivers, or those recovering from trauma.
- Vehicle Testing: Automobile companies use simulations for virtual crash tests and vehicle response analysis.
- Autonomous Vehicle R&D: AI models for self-driving cars are trained in virtual environments before real-world testing.
- Rehabilitation Therapy: Simulators are used in stroke and PTSD therapy to rebuild motor coordination.
- Traffic Behavior Research: Researchers simulate environments to study distracted driving, fatigue, or emergency responses.
Challenges in Graphic Engine Development
- Real-Time Performance: Rendering complex environments without lag.
- Hardware Requirements: High-fidelity simulations require powerful GPUs and CPUs.
- Synchronization: Ensuring accurate input-to-output response timing.
- Customization: Different regions require different road signs, traffic patterns, and environments.
Future Directions in Simulator Graphics
- VR and AR Integration for more immersive training.
- Eye Tracking & Emotion Sensing to adapt difficulty based on user stress levels.
- Cloud-Based Rendering allowing high-end simulations on low-end systems.
- AI-Enhanced Graphics that learn to simulate more realistic driver behavior and road scenarios.
These advancements aim to make simulators indistinguishable from real driving experiences.
Join the Conversation
Have you ever used a driving simulator for training or gaming?
Do you think simulation-based driving tests could replace real-world trials in the future?
What features would you love to see in the next generation of driving simulators?
Share your thoughts in the comments below!